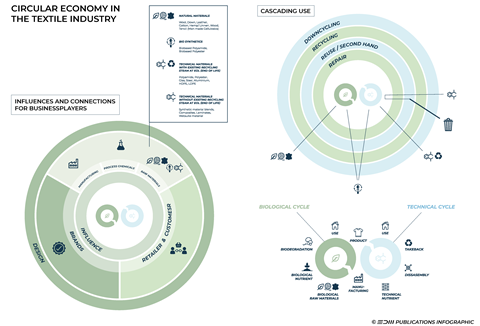
The principles of the circular economy in textile production are counter to the current linear “take-make-waste” process in the textile industry; exploiting resources for manufacture, finite product life, and one which ends with disposal.
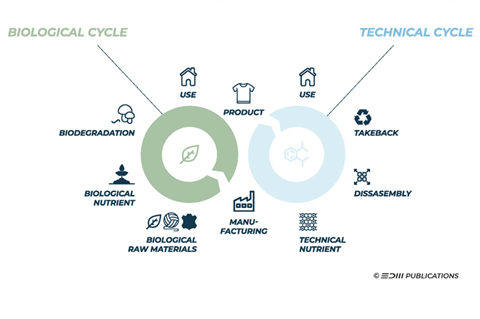
The circular economy differentiates between two types of circular loops: Biological and technical. In the textile industry, and in all circular economies, products should be designed and produced in a way that all its raw materials can be reintegrated into either one of the loops at the end of its life.
What are the two cycles of the circular economy?
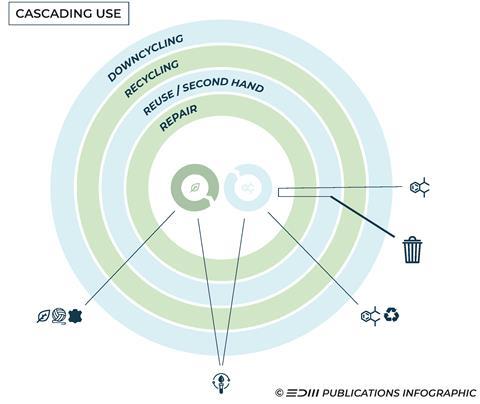
In circularity, a principal aim is to stop waste being produced in the first place. The same is true in textile production. and the textile industry In both the technical and biological cycles, products and materials are kept in circulation for as long as possible via reuse, repair, and remanufacture.
This cascading of products over as long a period as possible — by using materials that create the most economic value over multiple lifetimes — is an important factor in the responsible use of resources.
How can you design circular textiles?
Design has a central role to play when it comes to a circular textile industry. Textile products must be designed with circularity in mind. They should be:
- durable
- easy to repair
- easy to maintain
- made of components that can be replaced
- made from materials that can be easily recycled, for example mono-fibers.
Brands are a central link in the production chains (manufacturing, processing chemicals, and raw materials) as well as with retailers and consumers. They play a particularly important role in repair and take-back aspects.
Understanding the circular economy and the textile industry
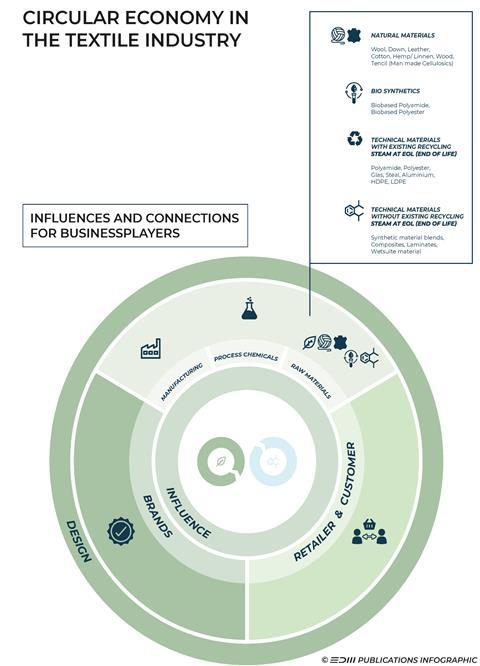
To view our Circular Business Graphic in one picture, just click on the image below to enlarge. Feel free to use and share the graphic but make sure to reference EDM Publications as the source.